revit design time lap
https://youtu.be/xOrB53h-ghA
ELIASH hyy good to see you here, what you want just search in above space hope you will find your answear
Task 1 of 4
Assess the constraints which need to be balanced to achieve the desired outcomes in an operational environment. Evaluate how these constraints correlate with each other and provide suitable examples from day-to-day operations to depict their interdependencies.
Task 2 of 4
Highlightdifferences and similarities between Operations management and Project management by giving relevant examples from open and multi-source industry sectors. Highlight importance of planning, monitoring and control in their methodologies.
Task 3 of 4
Assess the application of various modern operations management tools and techniques such as Kaizen, JIT, Six Sigma, Kanban and MRP, to functional areas such as (1) Inventory management (2) Manufacturing (3) Distribution and, (4) Logistics.
Task 4 of 4
Provide real life examples from organizations to show how they have achieved improvements in applying strategy, and enhancing efficiency and productivity through implementing benchmarks and best practices in the following operational areas:
Automation and technology
Capacity planning
Quality assurance and control
Warehousing and storage
Suggested Structure of your work:
Table of Contents
Introduction
Main Body
Start to answer the question considering all the points relevant.
Summary / Conclusion
References
Steps to quality monitoring our business operations to ensure our organisation remains competitive.are":
• Implement operational process improvements
•Measurement of the operative performance
•Collect relevant data
•Analyse all collected information
•Engage your employees
•Establish communication channels and strategies
•Implement new protocols and workflows
Planning is the most critical stage in any project. It guides the stakeholders, teams, sponsors, and project managers on how to go about the other project phases. It helps identify the goals, avoid missing deadlines, prioritizing essential tasks, reduce risks, and deliver the desired results.
Here are some compelling reasons why careful planning is essential in project management.
▪︎Clear Focus and objectives --
Break up the project into smaller tasks for the team to perform and achieve. This ensures everyone focuses on the project’s main goal.
A good project manager clearly defines the roles of all the team members to avoid any confusion and highlights roles that are interdependent. In case any confusion arises, the team can always go back to the plan to clarify.
▪︎Communication--
Proper planning facilitates communication. With proper communication, your team is aware of the tasks they need to perform and the deadlines set to accomplish them.
▪︎Task Dependencies--
Through planning, the project manager can identify tasks that are dependent on each other and schedule them accordingly.
▪︎Planning Resources Allocation--
Through effective planning, the project manager can procure enough resources for the project to run smoothly. This also allows him or her to allocate resources effectively and efficiently and avoid wastage in the long run.
Moreover, effective resource allocation enables the team to run the project within the budget line, often with some cost savings.
▪︎Risk Assessment--
You can’t know what challenges you might face in the course of the project if you don’t prepare yourself beforehand. However, a good plan allows you to conduct a risk assessment and establish contingencies to help you overcome them.
▪︎Planning Project Milestones --
A good plan must include milestones to help the project manager monitor the project’s progress.
Moreover, a good plan will also provide opportunities to re-evaluate deadlines, scope, and deliverables, thereby making adjustments where necessary.
Monitoring::
Project Monitoring refers to the process of keeping track of all project-related metrics including team performance and task duration, identifying potential problems and taking corrective actions necessary to ensure that the project is within scope, on budget and meets the specified deadlines.
When project managers make important decisions without verified data, it is like taking a stab in the dark. Your decisions will be based on very little to no evidence so the action may not be very efficient and could only be a waste of time and resources.
That’s why it is important to monitor projects diligently and use the data you gathered to come up with intelligent decisions.
Here are some questions answered through project monitoring:
Automated tools and technologies can simplify the tedious process of project monitoring. Most project managers have already adapted project management tools to delegate tasks and monitor their projects. However, project monitoring is a complex process and there are only a few project management apps out there that can support the project manager’s requirement to have laser-focus on individual tasks and team efficiency.
Control in their methodoligies::
The feature of project control for project management and they are
The project management methodologies list are:
•Waterfall methodology
•Agile methodology
•Scrum methodology
•kanban methodology
•scrumban methodology
•Extreme programming (XP) methodology
•Adaptive Project framework (APF) methodology
•Lean Methodology
•critical patg method
•Critcal Chain Project management
• New Product introduction
•Package enabled reengineering
•Outcome mapping
•Six Sigma
•PMI's PMBOK
•PRINCES2 Methodology
•Rapid application development methodologies.
1. Schedule
The operations manager has day-to-day management responsibilities and many of those tasks will take place on a business as usual schedule. vs. The project manager is responsible for ensuring that the project stays on time.
2. Budget
An operational manager is responsible for the department budget and the overheads related to running that department. vs. A project manager is responsible only for the budget relating to the particular project that he or she is working on at the time.
3. State
An operational manager has one single state to work with. vs. A project manager moves from one state to another i.e. results in change, moreover, the task is to become a perfect conductor between departments.
4. Period of time
An operational manager can not say about the real start and end points of his work. vs. A project manager has a definable start and end points (limited by the time of a project)
5. The main purpose
An operational manager is a product or process oriented vs. Obviously project orientation of a PM.
The similarities between porject managment and operation management are :-
* Both are performed by individuals.
* Both are planned , executed and controlled.
* Both are designed to meet the organizational and the strategic objectives.
* Both are subject to constrains such as schedule and resources.
Examples from and multi-sources industry sectors are:-
Task 3of 4
Kaizen ::
In our distribtion step to acheving sucess in modern distrubtion getting the basic right these business areas:
● Inventory Management
The just-in-time(JIT) inventory system is a management strategy that aligns raw-material orders from suppliers directly with production schedules. Companies employ this inventory strategy to increase efficiency and decrease waste by receiving goods only as they need them for the production process, which reduces inventory costs. This method requires producers to forecast demand accurately.
The JIT inventory system contrasts with just-in-case strategies, wherein producers hold sufficient inventories to have enough product to absorb maximum market demand.
JIT inventory management strategy has a number of potential benefits for businesses:
● Logistic
JIT applied to production systems increases the pressure on logistics, which needs to work with maximum efficiency. JIT methodology makes it essential for the relationship between different suppliers (raw material, components, services) and its B2B customers to be fluid, with open and efficient communication.
With the globalisation of markets, greater competitiveness and the boom in electronic commerce, consumers demand greater variety in products and reduced delivery times.
The Just-in-Time system has spread its application beyond production systems since just-in-time logistics is spoken of in customer service, order preparation inventory management and transport.
In supply chain management (SCM) it is necessary to have warehouses at those points in the chain where the goods have to stop, either to store them until they are sold or waiting for their distribution or temporary storage awaiting transport.
Warehouses also have to follow JIT principles, making it necessary to eliminate anything that could be considered to be unnecessary; speeding up picking tasks in the preparation of orders by using automated system which reduce inventory errors, speeding up tasks related to reverse logistics, optimising the routes for fork lift trucks or warehouse workers and using the most suitable metal racking systems for each level of rotation and goods flow.
● Distribution :
SIX SIGMA :-
Six Sigma (6σ) is a set of techniques and tools for process improvement. It was introduced by American engineer Bill Smith while working at Motorola in 1986. Jack Welch made it central to his business strategy at General ectric in 1995. A six sigma process is one in which 99.99966% of all opportunities to produce some feature of a part are statistically expected to be free of defects.
● Inventory Management :
Inventory management plays two critical roles in Lean Six Sigma. Firstly, the management of raw materials and semi-finished goods in the lean manufacturing process. Secondly, inventory control of finished goods held in a warehouse by manufacturers.
As a component of lean manufacturing, stock levels of raw materials and semi-finished products need to be controlled and managed.
This will reduce waste and optimize the production workflow.
Accordingly, Lean Six Sigma is used to identify and eliminate these root causes.
A. Lean Six Sigma in Action :
Root causes in inventory management can be described as higher and lower-level root causes. Often, excess stock, dead stock and obsolete inventory is caused by higher-level root causes. These include purchasing lead times, forecasting, quality and design issues. Consequently, these can then be broken down further into lower-level root causes.
B. Lean Inventory Management For the Future :
Just as Six Sigma evolved into Lean Six Sigma for today’s decade, it stands to reason that lean management principles equally apply to inventory management. This results in Lean Inventory Management principles for businesses outside of manufacturing. This is especially so for wholesalers, distributors and retailers who deal in physical goods.
Lean management, or Lean for short, is an approach to running an organization that supports the concept of continuous improvement.
Using lean principles in inventory management can result in quantifiable improvements for small and medium-sized businesses.
C. Principles of lean Inventory Management:
Like Six Sigma, there are five guiding principles in Lean Inventory Management. You can recognise some from past quality management and manufacturing principles of the past decades. Thus so, methodologies can adapt and evolve to suit pressing issues that businesses face today.
● Distribution :
Six Sigma is a data-driven approach to problem-solving.
The term “Normal Distribution Curve” or “Bell Curve” is used to describe the mathematical concept called normal distribution, sometimes referred to as Gaussian distribution. It refers to the shape that is created when a line is plotted using the data points for an item that meets the criteria of ‘Normal Distribution’.
The structure of a normal distribution curve. The center contains the value where the value of the greatest number of data points occur and therefore would be the highest point on the arc of the line. This point of the normal distribution curve is the mean or average.
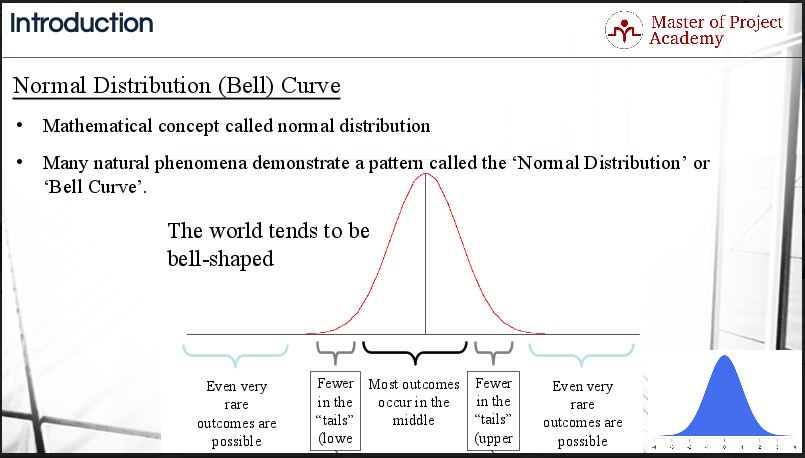
The normal distribution curve is one of the most important statistical concepts in Lean Six Sigma. Lean Six Sigma solves problems where the number of defects is too high. A high number of defects statistically equals high variation in the process. The normal distribution curve visualizes the variation in a dataset.
● Logistic :
Six Sigma Logistics has become the backbone for any business these days as it provides that important competitive advantage in the market, for any company. The Six Sigma approach of eliminating the defects or minimizing the variations in a process can be very handy if applied to logistics. This is because such an approach can increased the satisfactiob level of both external and internal clients and in turn can result in financial benefit.
• DMAIC or Define-Measure-Analyze-Improve- Control is one such method, devised for seamless assimilation of the Six-Sigma approach to logistics. It overhauls and improves the entire internal logistical process and ensures reduction of defects. It also reduces the mean route time and the route time variability.
• Variation reduction and logistics
In any business that involves logistics, variation reduction is an important concept. Logistics is all about managing inventory and this depends heavily on managing variance.
It is evident that for Six Sigma to be successful in logistics, it should be driven with a sustained focus on quality improvement and customer relations.
MRP ::
Material requirements planning (MRP) is a production planning, scheduling and inventory control system used to manage manufacturing processes. Most MRP systems are software-based, but it is possible to conduct MRP by hand as well.
●Inventory management
Material requirements planning (MRP) is a computer-based inventory management system designed to assist production managers in scheduling and placing orders for items of dependent demand. Dependent demand items are components of finished goods—such as raw materials, component parts, and subassemblies—for which the amount of inventory needed depends on the level of production of the final product.
The first MRP systems of inventory management evolved in the 1940s and 1950s. They used mainframe computers to explode information from a bill of materials for a certain finished product into a production and purchasing plan for components. Before long, MRP was expanded to include information feedback loops so that production personnel could change and update the inputs into the system as needed.
● Manufacturing :
A critical input for material requirements planning is a bill of materials (BOM) —an extensive list of raw materials, components, and assemblies required to construct, manufacture or repair a product or service. BOM specifies the relationship between the end product (independent demand) and the components (dependent demand). Independent demand originates outside the plant or production system, and dependent demand refers to components.
Companies need to manage the types and quantities of materials they purchase strategically; plan which products to manufacture and in what quantities; and ensure that they are able to meet current and future customer demand—all at the lowest possible cost. MRP helps companies maintain low inventory levels. Making a bad decision in any area of the production cycle will cause the company to lose money. By maintaining appropriate levels of inventory, manufacturers can better align their production with rising and falling demand.
● Distribution
Material requirements planning (MRP) and distribution requirements planning (DRP) calculates organization-specific net requirements from gross requirements by evaluating:
MRP Logistics in the business of cargo movements on Door-to-Door basis through Air, Train and Surface and delivering goods. We have our team of logistics professionals and many companies are availing our services in logistics solutions. They are getting hassle free logistics services enable them to concentrate on their competitors. We are also proving door-to-door local deliveries to many companies dealing in the business of information technology.
Kanban ::
Kanban definition. Initially, it arose as a scheduling system for lean manufacturing, originating from the Toyota Production System (TPS). In the late 1940s, Toyota introduced “just in time” manufacturing to its production.
Kanban is a workflow management method for defining, managing and improving services that deliver knowledge work. It aims to help you visualize your work, maximize efficiency, and improve continuously. From Japanese, kanban is translated as billboard or signboard. Originating from manufacturing, it later became a claimed by Agile software development teams.
● Inventory Management
Kanban isan inventory scheduling system that allows companies to stock only needed components and arts in the production or distribution process. In lean manufacturing, the process pulls materials through the production or distribution process. The Kanban system provides a signal for reordering or replenishing stock.
The goal of a Kanban inventory system is to continually maintain the minimum amount of stock. The beauty of the way the supermarket managed its inventory was that it only stocked items it expected to sell them in a given time.
It is a tool for lean manufacturing that aims to prevent inventory pileup by initiating production only to restock empty reserves.
● Distribution ::
Kanban isan inventory scheduling system that allows companies to stock only needed components and arts in the production or distribution process. In lean manufacturing, the process pulls materials through the production or distribution process. The Kanban system provides a signal for reordering or replenishing stock.
●Logistic ::
The literal translation of Kanban in Japanese is “signboard.” This is because, originally, poster board cards were used to request the parts that were needed from the previous process.
Advangtage of the kanban method in logistics and production :
The Kanban system is a perfect match for the just-in-time method because it:
Technologies are a vital part of R&D. Nestle engineers working in R&D in a variety of fields – from packaging and equipment, to food processing technologies and manufacturing new beverage systems such as Nespresso, Nescafé Dolce Gusto, Special. T and BabyNes.
Alongside engineers, of food scientists develop processes and technologies that enable the development of safe, nutritious foods and beverages while keeping us on the cusp of new developments in food science and technology.
Nestlé has developed, and/or is a world-leader in a large number of different technologies. Here are a few examples:
Capacity is the total maximum level of output a business can produce in a given period. This allows a business to meet the level of demand for a product.
Capacity utilisation is the actual output per annum.
Capacity planning is the process of determining the production capacity needed by an organization to meet changing demands for its products. In the context of capacity planning, design capacity is the maximum amount of work that an organization is capable of completing in a given period. Examples of this is the seasonality of products.

A sound automation strategy begins by conducting a thorough assessment of existing business processes. It begins with a look at tasks and procedures that are highly labor-intensive, especially those that add little value. Tasks are that are the most time- and labor-intensive are those that are the top targets for automation.
Many producers already have systems that are automated and integrated, operating on a common network or platform. However, full integration is the optimal state, where all systems across the enterprise are connected, with data shared across the organization.
Packaging, in particular, is an area where fully implemented integration has been elusive. Individual components and machines are integral parts of many such packaging systems. When one of those components is offline due to maintenance or repair, the entire packaging system can halt.
Integrating the whole system greatly lessens the reliance on one component and the unfortunate consequences that arise when that component breaks down.
User-friendly automation systems are critical. Without them, there are likely to be higher training costs, especially as food and beverage manufacturing traditionally relies on an older workforce. Automation should use software that is easy to learn, use, and master to make adoption as frictionless as possible.

Many food producers still rely on manual processes. Automation can reduce production costs by identifying inefficient and low-profit procedures.
Today, employees, leaders, and key stakeholders can be anywhere, using multiple device types to connect to systems. Increasingly, these devices are mobile. Your automation systems need to support multiple devices and be accessible and functional across platforms. Data needs to be easily accessible from mobile devices and not bind employees to their desks in order to access features.
It’s important for manufacturers to establish measures, including key performance indicators that measure the impact and efficacy of the automation solutions that are implemented. Whether these measures reflect shortened lead times, less waste, shorter production cycles, fewer processing costs, or lower personnel costs, the need for measures against baselines should be determined, tracked and used.
These measures can inform not only performance but also, other opportunities for improvements and future purchases.
Many vendors provide valuable incentives for early payment discounts. These discounts can considerably reduce project costs, making the choice about adoption clearer for companies debating whether to fully invest.
NexTec Group helps companies identify the enterprise resource planning (ERP) tools necessary to integrate automation across the food and beverage company. With ERP, companies pull together data from operational, financial, sales, and customer relations areas, providing holistic looks at the information, reporting, and analysis necessary to improve operations.
We help companies find the right ERP solution to fit the needs, budgets, and automation tools in place and planned. Download the NexTec Ebook – Reduce food waste and improve to learn how NexTec can help select and implement an ERP solution that drives results.
The limit sedimentation velocity of a particle is its theoretical descending speed in clear and still water. In settling process theory, a particle will settle only if :-
Removal of suspended particles by sedimentation depends upon the size, zeta potential and specific gravity of those particles.
Water disinfection means the removal, deactivation or killing of pathogenic microorganisms. Microorganisms are destroyed or deactivated, resulting in termination of growth and reproduction. When microorganisms are not removed from drinking water, drinking water usage will cause people to fall ill.
Disinfection can be attained by means of physical or chemical disinfectants.
For chemical disinfection of water the following disinfectants can be used:
- Chlorine (Cl2)
- Chlorine dioxide (ClO2)
- Hypo chlorite (OCl-)
- Ozone (O3)
- Halogens: bromine (Br2), iodene (I)
- Bromine chloride (BrCl)
- Metals: copper (Cu2+), silver (Ag+)
- Kaliumpermanganate (KMnO4)
- Fenols
- Alcohols
- Soaps and detergents
- Kwartair ammonium salts
- Hydrogen peroxide
- Several acids and bases
For physical disinfection of water the following disinfectants can be used:
- Ultraviolet light (UV)
- Electronic radiation
- Gamma rays
- Sounds
- Heat
2.Rainwater harvesting (RWH) is the collection and storage of rain, rather than allowing it to run off. Rainwater is collected from a roof-like surface and redirected to a tank, cistern, deep pit (well, shaft, or borehole), aquifer, or a reservoir with percolation.
A rainwater harvesting system has three main stages
1) Collecting & transporting rainwater
This is done through catchment areas & conduits. The catchment of a water harvesting system is the surface which receives rainfall directly.
It can be a paved area like the terrace or courtyard of a building. Conduits are the pipelines that carry rainwater from the catchment or rooftop to the harvesting system.
Filtration
A filter unit is a chamber filled with filtering media to remove debris and dirt from water before it enters the storage tank or recharge structure.
3) Storage in tanks for reuse / Recharging the groundwater levels
The harvested water can now be stored in storage tanks for immediate usage, which are designed according to the water requirements of the society.
Existing non-potable water storage tanks in the society can also be used to store the harvested rainwater.
Transformational leaders are able to lead through adaptation of their organization to changes within the environment of operation. Thus, change can never occur without planning and execution. Leaders must know that a real change occurs in the character of organizational stakeholders. Any failure to realize this will only provide a cosmetic and short-lived change experience. Thus, a transformation leader must be able to progressively restructure an organization by eliminating approaches, which do not properly work. However, it is vital to keep those methods, which contribute to implementation of new cultures, structures and systems. This will require the leader to be able to identify, improve and utilize the complete potential of the employees. The leaders must also be able to align cultural and structural processes with the organizational goal.
Idealized Influence – This entails being able to build confidence and earn the respect and trust of the members of one’s organization. By being a charismatic leader, followers will be more adaptive to changes when the need arises.
Inspirational Motivation – With enthusiasm and positivity, a leader will be able to motivate followers to become team players and dreamers that things are possible.
Intellectual Stimulation – Transformational leaders challenge members of the team to solve problems that arise and teach them to be creative and innovative by stimulating their minds. These allow members to voice out ideas and share their views without having the fear of being punished or reprimanded.
Individualized Consideration – With accepting the differences among employees, a transformational leader know the importance of addressing problems of workers accordingly, mentoring and offering individualized career counseling.
(A) sundar pichai :-
Importance of a Leader:
Leadership is an important function of management which helps to achieve organizational goals.
The following points justify the importance of leadership.
• Leadership Provides Future Vision: A successful leader creates a clear vision for the future and finds the best way to approach it.
• Leadership helps in managing organizational change: An effective leadership is essential for managing organization.
• Leadership helps in business understanding: It helps to develop awareness of the strengths, weaknesses and opportunities in the organization. • Leadership helps in encouraging new ideas.
He is known to be incredibly humble person at heart with an impossible dreams of advancement, improving access, and internet connectivity for underdeveloped countries.
Sundar Pichai practices what he preaches and one of his major leadership strategy is to see other people succeed and not only himself. By setting up collaborative cultures Sundar has successfully incorporated this leadership strategy throughout Google.
Following are the leadership qualities of Sundar Pichai:
a. He believes in success of others. He wants other people to be successful and help them by removing road blocks and he believes in team work
b. He has a vision of what he wants to achieve and the ability to clearly communicate his vision so that everyone in the organization understands what is needed to achieve the vision.
c. He has a willingness to take on new challenges, take calculated risks, make tough decisions, and be willing to go out on a limb for something they believe in. Transformational leaders have the courage to create a vision and make the difficult decision necessary to achieve their vision.
d. He is fuelled with passion from within. Transformational leaders have passion and motivation that people can sense and feed off of it.
e. Transformational leaders, based on their personal passion, have the ability to inspire others and get them to buy into their vision and execute it on all levels of the company.
f. While it is a bit cliché, actions do speak louder than words and when leaders live according to the standard they set, people take notice. Leaders often promise a lot, but it is the follow through that has a true impact on a leader’s ability to evoke change and get buy in
g. Transformational leaders model a company standard they expect everyone to follow. He clearly communicate their vision, expectations, and how this standard is to be carried out throughout the organization.
CONCLUSION: Transformational leadership represents the essential quality for successful management of transformational organizational changes. It is about the quality that, in fact, so called transactional management has missed to bring to an end of the transformational cycles with efficiency. In that sense, the success in realizing transformational organizational changes means that the key people in an organization (managers) develop sets of appropriate skills and attributes that are characteristic to so-called transformational leaders.
(B) Sheikh Mohammed Bin Rashid Al Maktoum :-
(C) Mukesh Ambani :-
4no. Answer:-
(A)Bashar Al- Assad
(1) 191,000 people killed and counting:-
The main thing you need to know about Assad is that his regime is responsible for killing a huge number of people.
According to the United Nations, at least 191,000 people were confirmed killed in Syria as of April 2013. More than 8,800 were children under the age of 10.
Keep in mind that these are just "confirmed" numbers. And they are based on nearly 320,000 reported killings. The death toll is likely much higher than even that. As Navy Pillay, the UN High Commissioner for Human Rights, said, "Tragically it is probably an underestimate of the real total number of people killed during the first three years of this murderous conflict."
Rights Watch (HRW) calls the vast and complex network of torture and detention maintained by Syrian security forces and intelligence agents.
"The level of torture is not comparable to any other conflict I've worked on," Anna Neistat, associate director for Program and Emergencies at HRW, told GlobalPost in 2012.
When it comes to Assad's thugs, it seems that no person is too young to be tortured. One in five detainees is a minor, says HRW.
GlobalPost spoke with some of the children tortured and imprisoned by the regime. Their stories are horrifying.
There's no shortage of war crimes when it comes to the Assad regime, but one of the more prominant violations has been the use of chemical weapons. Before the United States started bombing the Islamic State, the closest it came to striking Syria was after Aug. 21, 2013, when someone — there's international consensus that Assad's forces were the aggressors, although the regime continues to deny it — dropped weapons loaded with sarin gas on Ghouta, a rebel-held suburb outside Damascus.
More than 1,400 Syrian civilians were killed in the attack, and several hundred more were poisoned. It was the first large-scale use of chemical weapons since 1988, when Saddam Hussein used them against the Kurds near the end of the Iran-Iraq War.
Barack Obama famously warned that Assad would be crossing a "red line" if he used chemical weapons against his own people, but the United States didn't take military action and Obama probably wishes he could take that warning back.
are like chemical weapons in that they don't discriminate between civilians and soldiers, and, one could argue, this is their main value: killing huge numbers of civilians, destroying whole city blocks, and terrorizing the entire population. These bombs are highly explosive, unguided, and imprecise weapons made from cheap and available materials, like oil or water drums, and packed with explosives and scrap metal for maximum destruction.
Assad's army has repeatedly used barrel bombs, and in densely populated cities like Aleppo, the results have been devastating to human life and city infrastructure.
The scale of killing is massive. The total horror of the Assad regime, though, often reveals itself at a small scale. Take the massacre in the town of Houla.
There, according to a UN report, Syrian government forces and fighters from the brutal, pro-government militia known as the "Shabiha" ("ghosts" in Arabic) killed more than 100 civilians in May 2012. Half of the victims were children. There were reports of armed gunmen spraying homes with indiscriminate weapon fire and going house to house to kill the men, women, and children inside.
The massacre prompted the UN Human Rights Council to pass a resolution condemning the regime for its deliberate attacks on civilians.
If you feel like getting inside the head of a Shabiha fighter — not that you'd really want to — read this GlobalPost interview.
The US fight against the Islamic State will always be bound up in the videotaped beheadings of American journalists James Foley, who worked for GlobalPost, and Steven Sotloff.
Rebel groups like Al Nusra and the Islamic State have played a large role in turning Syria into "the world's most dangerous country for journalists," according to Reporters Without Borders (RSF), but the Assad regime has been a major player, too. Assad's forces have consistently arrested, imprisoned, and killed journalists throughout the duration of the conflict.
Marie Colvin, an American reporter for the Sunday Times, was among the journalists killed while covering the war. She was killed alongside a prominent French photographer, Remi Ochlik, when the regime bombed a house where she was staying in the city of Homs. French President Nicolas Sarkozy claimed at the time that they'd been "assassinated," since the house was serving a well-known press center.
Starbucks Corporation in the Global Market
Depending on the theories and materials you studied during this mini semester, analyze the case study of Starbucks Corporation.
Suggested areas you need to discuss:
The nature of the external and internal environment surrounding Starbucks.
Analyze Starbucks strategic Vision, Mission, and Core Values.
What is Starbuck’s strategic approach to gain competitive advantage
Analyze the overall Starbuck’s strategy using Porter’s Five Forces Model Competition
Choose one country that Starbucks’s considered to be strong and conduct a PASTEL analysis for that country.
Choose another country that Starbucks does not operate in at this time and suggest a strategic entry plan to operate in that country.
Starbucks imports coffee beans from different countries and each of these countries has its own tariff and customs regulations. In addition, any political upheavals in the countries where Starbucks imports its coffee beans would greatly interfere with the company’s operations.
The global financial crisis of 2008 greatly affected the operations of Starbucks in various countries. The recession resulted in an increase in the operational costs of the company The coffee industry is demand- driven and when economic conditions are harsh, consumers treat coffee as a luxury and this affects sales
iii)Socio-cultural environment
Consumers across the world are increasingly demanding fair practices, and this has seen many firms change their operating practices in order to accommodate these demands.The company has also had to adjust its product offerings in order to meet the growing demands of the rising number of educated and health conscious consumers.
iv)
Advances in technology affect product innovation, product services, customers’ store experience, and the way organizations are able to interact with other business partners. Technological improvements can enable a company to market its products directly to their target market using emails, text messages, and social network sites as well Throughthe use of technology, Starbucks has managed to change its product mix to suit new market segment
v)
The two main competitors of Starbucks are MacDonald’s McCafe and Dunkin Donuts. On the one hand, McCafe maintains a low price strategy o its products in Burritt, 2007. On the other hand, Dunkin Donuts offers customers a variety of coffee flavors to choose from, in addition to its emphasis on quality in Dicarlo, 2004.
Starbucks provides interpersonal services to its customers in whereby there is high contact between baristas, staff, and customers (Miller, 2010).. The company has tried to change the formula of some of its products to suit the tastes and preferences of customers in certain markets The management at Starbucks recognizes the important role played by the staff and Baristas, which is why they offer rewards and incentives in recognition of their exemplary work.
Starbucks boasts of a wide variety of over 30 coffee products that customers can choose from. The company is always introducing novel products in the market to suit the changing demands, tastes and preferences of its growing customer base.
Starbucks’ products are priced at a premium owing to the perceived upscale image in the eyes of the consumers. In this case, Starbucks uses high pricing to differentiate itself from the rest of the competition
Most Starbucks coffee stores are located in neighborhoods with high traffic. The company’s coffee stores are also located in different large chains. The “third place” concept as practiced by Starbucks has helped to turn its stores into an ideal uenvironment away from home where customers can relax, surf the internet, or listen to music
One of the fundamental requirements for successful promotion is to facilitate friendly and smooth interactions among the company’s representatives and the market without compromising the efficiency manner in which a company is able to offer its services to the target market.
The success of any service firm largely depends on the ability of the organisation in question to target, acquire, get hold of, and retain keep the ‘right’ customers. Good organisations are mainly based on cultivating customer retention relationships, as opposed to the acquisition/transaction mentality. Starbucks is one such organisation.
link- https://ivypanda.com/essays/starbucks-5/
2.Analyze Starbucks strategic Vision, Mission, and Core Values.
Mission-Starbucks Coffee’s corporate mission is “to inspire and nurture the human spirit – one person, one cup and one neighborhood at a time.” This mission statement reflects what the company does to keep its business running. It is clear that target consumers are given emphasis in this corporate mission. The following components of Starbucks’s corporate mission statement influence strategic management in growing the business:
they are performance driven, through the lens of humanity.
link-. http://panmore.com/starbucks
Starbucks strategy is a simple saturate the market. By spreading out the outlet location it makes one store not cut the profits of another store. Usually, the stores would be placed on locations based on demographics, traffic patterns, the location of competitors as well as the location of its own stores.
However, the Starbucks strategy went against the grain. Instead of following the trend, CEO Howard Schultz had a different idea. He decided that the Starbucks strategy would be to blanket an area completely. Siding matter about one store cut the profits of another store, the Starbucks strategy focused on heavily increasing the foot traffic in one specific part of town. They think this will reduce the company’s delivery and risk, also the customer doesn’t need to stay in the waiting line for a long time. Schultz knew that his Starbucks strategy was a risk, but it was one he was willing to take.
For the result of this strategy. Starbucks quickly achieve market dominance. They have more than 20 million customers per week, this is the highest frequency of visiting customers. Since the company went public, sales have risen roughly 20% each year. Even when the rest of the economy seems to be in a slump, loyal patrons keep returning to Starbucks for their regular cup of Joe.
Starbucks using many kind of entry mode for expanding its business to another country. These include joint ventures, licensing, and wholly owned subsidiaries. Starbucks gain advantage of providing access to local partner knowledge by using joint venture. Starbucks also shares development costs and risks with Sazaby in addition. Starbucks use licensing way to enter the Middle East because with this mode it allow Starbucks to minimize capital outlays for marketing research and decrease local market expertise. And for the wholly owned subsidiaries it offers technology protection and ability to engage in the global strategic coordination.
now a days they became international Because of its high growth in major reason, Starbucks initiate international expansion. Starbucks adopted a strategy that characterizing through low local responsiveness and price considerisation. In the 1996 Starbucks start to grown in Japan through joint venture, and then it expand to Europe and the Middle East using the same way.
link-https://www.ukessays.com/essays/marketing/strategy-and-competitive-ad6vantage-of-starbucks-marketing-essay.php
4.Analyze the overall Starbuck’s strategy using Porter’s Five Forces Model Competition
The strong force of competition is the combined effect of the external factors identified in this Five Forces analysis. In this regard, the most significant forces for Starbucks Coffee Company’s strategic consideration are competitive rivalry, the bargaining power of customers, and the threat of substitutes. Still, the other forces also influence the company’s business performance. In summary, the following are the intensities of the Five Forces in Starbucks Corporation’s industry environment:
tarbucks faces the strong force of 6competitive rivalry In the Five Forces analysis model, this force pertains to the influence of competitors on each other and the industry environment. In this case of Starbucks Coffee Company, the following external factors contribute to the strong force of competition:
this force as the influence that suppliers have on the company and its industry environment. The following external factors contribute to the weak bargaining power of suppliers on Starbucks Corporation:
this force refers to the effect of new players or new entrants in the industry. In this business case, the following external factors contribute to the moderate threat of new entrants against Starbucks:
This component of the PESTEL analysis model refers to the economic conditions and changes significant to business. Starbucks faces the following economic external factors in its remote or macro-environment:
The high economic growth of developing countries and the declining unemployment rates create opportunities for Starbucks to gain more revenues from various markets around the world.
This aspect of the PESTEL analysis framework shows the social conditions and trends influencing consumers and business. Starbucks must address the following social/sociocultural external factors in its remote/macro-environment:
Starbucks has opportunity to increase its revenues based on increasing demand for specialty coffee, which is due to a growing coffee culture and a growing middle class around the world. Also, the company has the opportunity to widen its array of more healthful products to attract health-conscious consumers to Starbucks cafés. Thus, all the identified external factors in this component of the PESTEl analysis model present opportunities for Starbucks Coffee.
In this part of the PESTEL analysis model, technologies and related trends are identified. Starbucks experiences the following technological external factors in its remote/macro-environment:
Starbucks has the opportunity to improve its mobile apps and linked services to gain more revenues through mobile purchases. The company also has the opportunity to improve its supply chain efficiency based on new technologies coffee farmers use. However, the rising availability of home-use specialty coffee machines is a threat to Starbucks because it increases the availability of substitutes to Starbucks products.
This component of the PESTEL analysis model identifies the effects of ecological or environmental conditions and changes on business. Starbucks faces the following ecological/environmental external factors in its remote or macro-environment:
The business sustainability trend focuses on business processes that ensure minimal environmental impact. In relation, responsible sourcing emphasizes corporate social responsibility in the supply chain. Starbucks has opportunities to enhance its performance in these areas. Note that the company already has responsible sourcing policies. Starbucks also has the opportunity to offer more of its products in recyclable packaging.
The legal factors in the PESTEL analysis model are the laws and regulations on business. Starbucks must address the following legal external factors in its remote/macro-environment:
Starbucks has opportunities to improve its performance by satisfying product safety regulations and regulations on ingredients from genetically modified organisms (GMOs). Starbucks is already performing well in these aspects. However, increasing employment regulation, especially in developing countries, threatens Starbucks Coffee’s access to the labor market. This external factor also impacts Starbucks through increased spending for human resources. Thus, in this aspect of the PESTEl analysis model, the identified external factors present mostly opportunities for Starbucks Coffee.
link-. http://panmore.com/starbucks-coffee-pestel-pestle-analysis-recommendations
6.Choose another country that Starbucks does not operate in at this time and suggest a strategic entry plan to operate in that country.
well as we know still there are many countries don't have Starbucks,The farthest we can get from a Starbucks on Earth is off the coast of South Africa. With the exception of the three locations in Morocco and 18 in Egypt, there are no Starbucks in continental Africa,and also in Baltic State there isn't Starbucks
if we start Starbucks by considering the above mentioned one country such as BALTIC STATE, we must first realize that Starbucks does not sell independent. They give license to like minded business man to open licensed Starbucks store along with the other business that they run. It is very important to select the position where we want to have such a Starbucks store.
strategic entry plan to operate Starbucks Globalisation and technology as the two core macro environmental elements of business settings have imposed and aided companies’ international expansion strategies and tactics. As such, success beyond the national borders of a corporation is not only an indicator of success, it has ultimately become necessary for survival in a competitive market carefully evaluate all factors influencing the decision regarding the area of expansion and the entry mode of the company in the new region
i) factors, country specific factors and market specific factors. Although their categorisation of factors is valid in the strategic management of internationalisation of firms
ii)quality of the products or operations of coffee shops that trade under their company name is significantly lower than in the case of joint ventures or wholly-owned subsidiaries.
iii) Starbucks, are able to determine the best mix of entry modes specific to the regions where the expansion is taking place in order to become global leaders
iv)need to take into account any cultural aspects of the countries where their subsidiaries are. As such, Starbucks adapts their food and beverage offerings in their cafés in order to suit their customers’ taste
The company that reinvented the way in which people enjoy their traditional cup of coffee, Starbucks has conquered the globe in less than half a century,focus is on creating long-lasting relationships with consumers in every geographical region, seeking and rewarding the loyalty of the brand’s
link-. https://www.ukessays.com/essays/marketing/starbucks-international-entry-methods-marketing-essay.php